How to Publish Multilingual Content
Overview
When working on SEO, it’s a common scenario to target different countries and regions for promotion. As a result, we often consider creating content in multiple languages. However, this differs slightly from building a website—we can’t simply translate an article into different languages. People in different countries and regions have unique customs, ways of referring to things, and even search intentions. This means that when creating content in certain languages, we should research keywords specific to that market and write the content in the corresponding native language.
Common Domain Strategies for Multilingual Websites
There are generally three common domain strategies we use:
- Subdomain: Easy to optimize SEO independently, but requires more maintenance.
- Subdirectory: Concentrates SEO authority on the main domain, simpler to manage.
- Top-level domain: Offers the best localization, but comes with higher costs.
Subdomain
When using subdomains to distinguish languages, the domain structure looks like this:
Main language domain: https://example.com
Japanese domain: https://jp.example.com
German domain: https://de.example.com
Subdirectory
With the subdirectory approach, the domain structure looks like this:
Main language domain: https://example.com
Japanese domain: https://example.com/jp
German domain: https://example.com/de
(Note: The ‘jp’ and ‘de’ in the path typically represent language or region codes, making it easier for users and search engines to identify.)
Top-Level Domain
With the top-level domain approach, the domain structure looks like this:
Main language domain: https://example.com
Japanese domain: https://example.jp
German domain: https://example.de
How to Best Combine Different Domain Strategies with QuickCreator
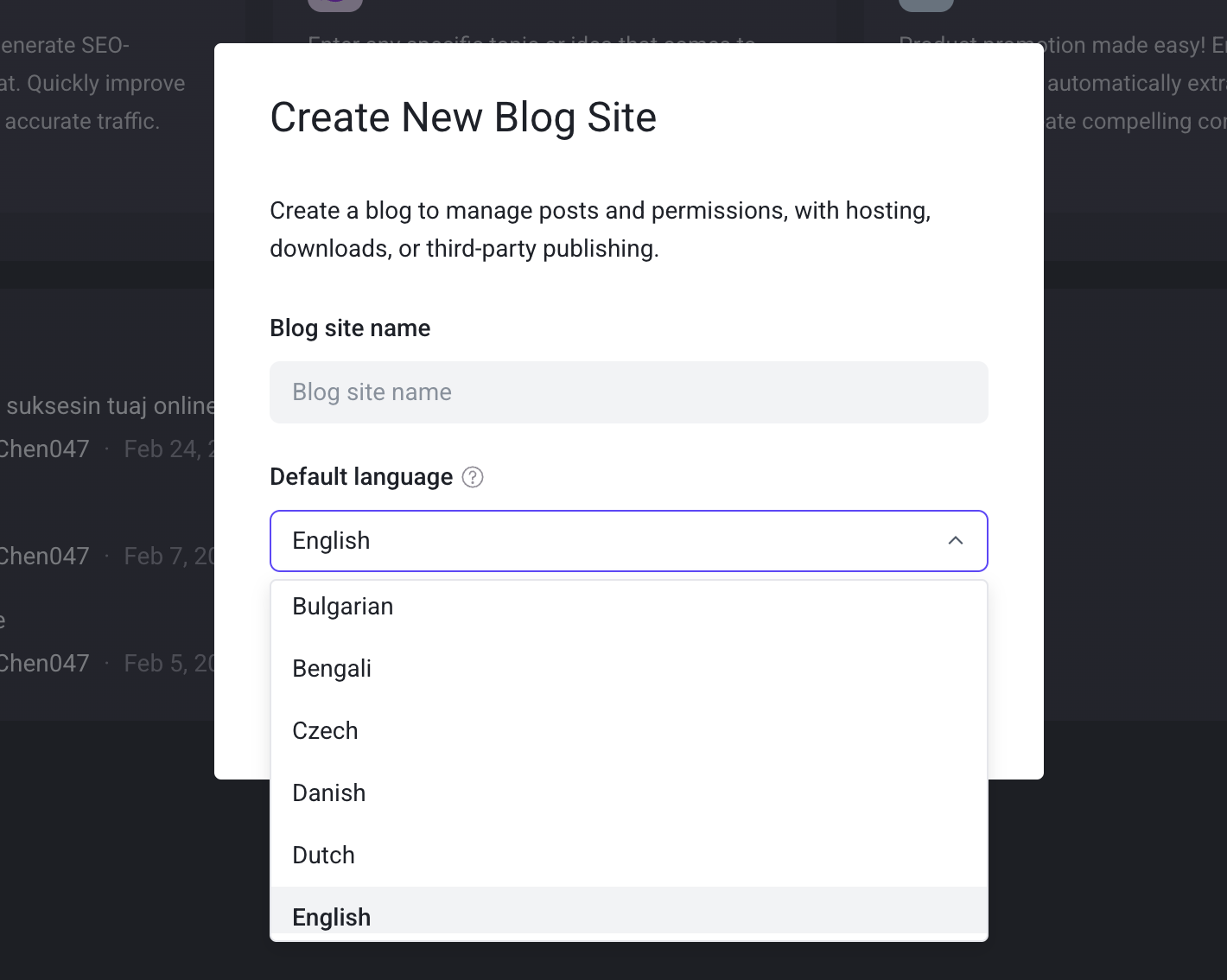
1.Create Separate Sites for Different Languages in QuickCreator
When creating a site, select the language, and QuickCreator will perform two key actions:
- Automatically configure metadata (e.g., language tags) when publishing articles to optimize SEO.
- Provide language-specific default settings during the writing process (e.g., keyword suggestions or formatting templates). When you write articles, these default language settings will apply throughout the entire workflow, saving you from repeated configurations.
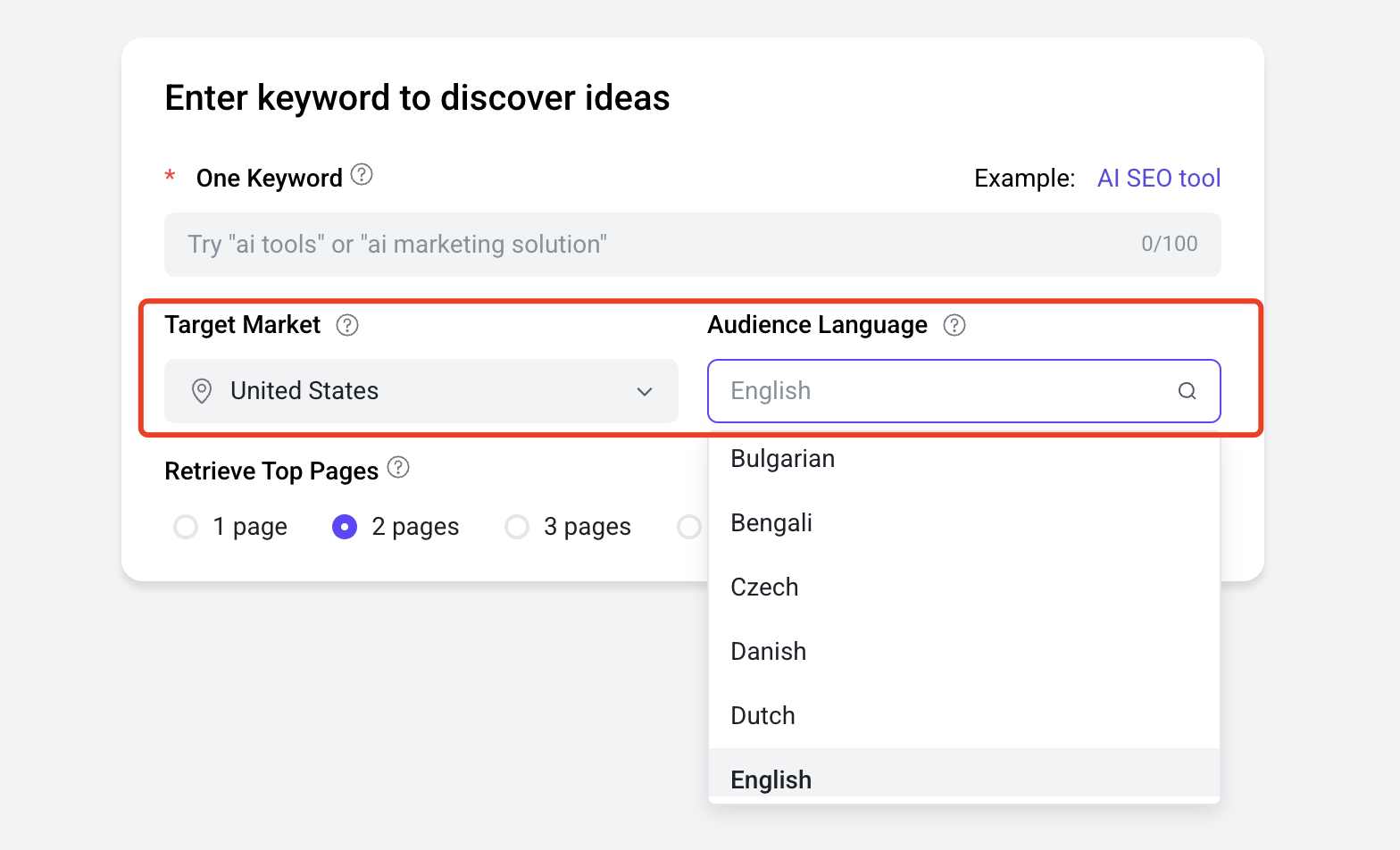
2.Write Content Separately for Each Language Site
As mentioned earlier, the search intentions of people in different countries and regions are not entirely the same. Therefore, we recommend conducting targeted keyword research for each local market and writing distinct content. Avoid directly translating documents into different languages, as search engines prefer original content tailored to local search intent. As shown, QuickCreator supports configuring the target market and language when generating content:
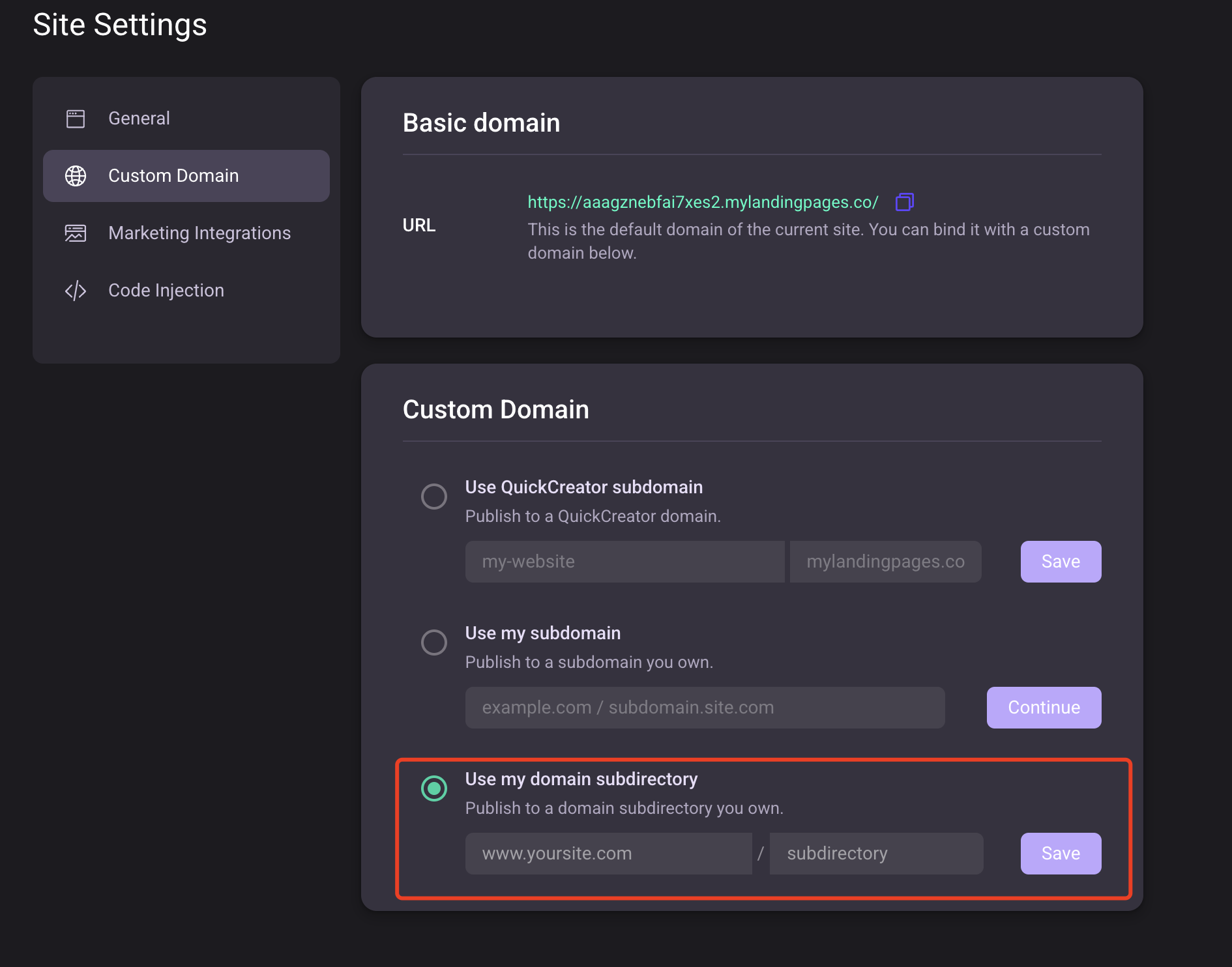
3.Custom Domains
When binding domains for multilingual sites, we generally recommend using the subdirectory approach. Configure each language-specific site once, as shown below:
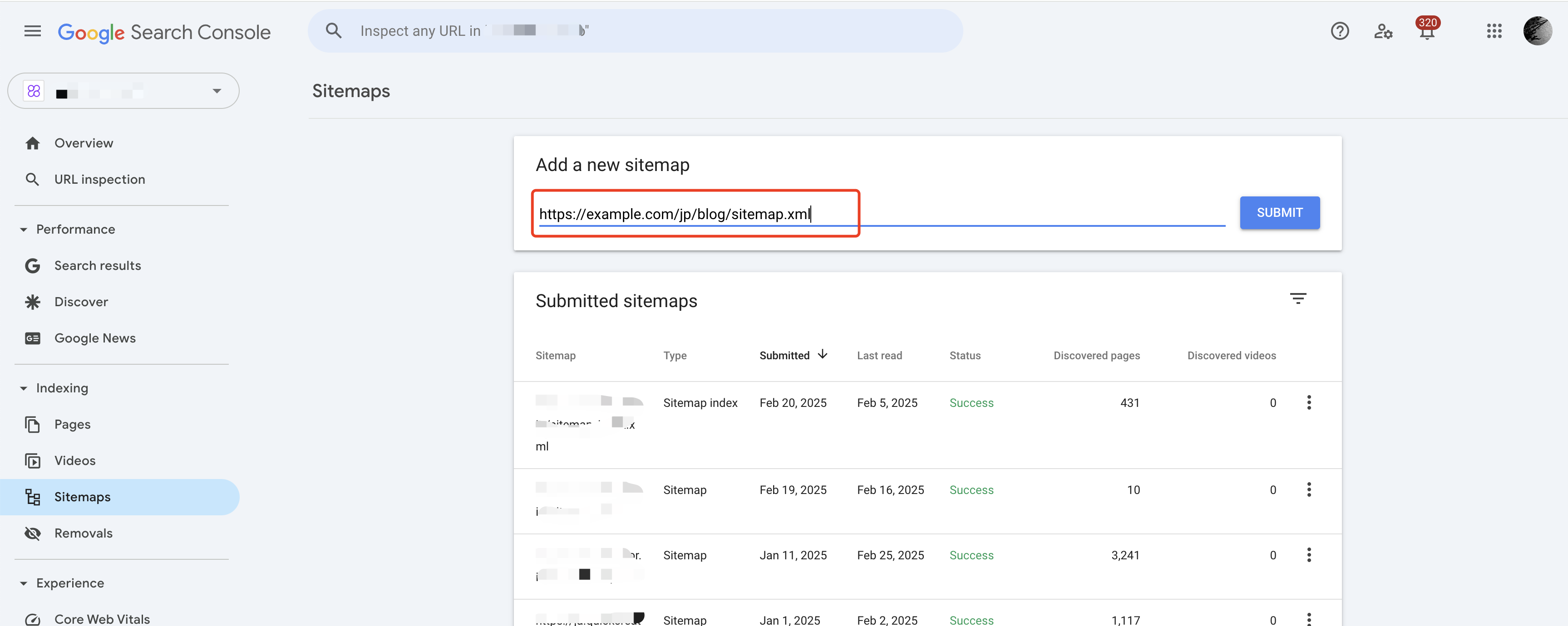
4.Submit Sitemaps for Each Site Separately to Google Search Console
To ensure faster indexing and facilitate data tracking and analysis later, you should submit a sitemap file for each language site. Make sure the Sitemap includes the full URLs for each language site, such as example.com/jp/sitemap.xml。。